ctr run流程
我们接下来从TaskService的Create接口看起,看一下containerd是如何与底层的containerd-shim以及最后的runc进行结合工作的。
opts := runtime.CreateOpts{
Spec: container.Spec,
//这看起来实际操作I/O还是底层的容器执行器
IO: runtime.IO{
Stdin: r.Stdin,
Stdout: r.Stdout,
Stderr: r.Stderr,
Terminal: r.Terminal,
},
Checkpoint: checkpointPath,
Runtime: container.Runtime.Name,
RuntimeOptions: container.Runtime.Options,
TaskOptions: r.Options,
}
c, err := runtime.Create(ctx, r.ContainerID, opts)
// Create a new task
func (r *Runtime) Create(ctx context.Context, id string, opts runtime.CreateOpts) (_ runtime.Task, err error) {
namespace, err := namespaces.NamespaceRequired(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := identifiers.Validate(id); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "invalid task id")
}
ropts, err := r.getRuncOptions(ctx, id)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// newBundle 根据传入的路径和 ID 创建目录文件,/var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v1.linux/default
bundle, err := newBundle(id,
filepath.Join(r.state, namespace),
filepath.Join(r.root, namespace),
opts.Spec.Value)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer func() {
if err != nil {
bundle.Delete()
}
}()
shimopt := ShimLocal(r.config, r.events)
if !r.config.NoShim {
var cgroup string
if opts.TaskOptions != nil {
v, err := typeurl.UnmarshalAny(opts.TaskOptions)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
cgroup = v.(*runctypes.CreateOptions).ShimCgroup
}
exitHandler := func() {
log.G(ctx).WithField("id", id).Info("shim reaped")
t, err := r.tasks.Get(ctx, id)
if err != nil {
// Task was never started or was already successfully deleted
return
}
lc := t.(*Task)
log.G(ctx).WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"id": id,
"namespace": namespace,
}).Warn("cleaning up after killed shim")
if err = r.cleanupAfterDeadShim(context.Background(), bundle, namespace, id, lc.pid); err != nil {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err).WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"id": id,
"namespace": namespace,
}).Warn("failed to clean up after killed shim")
}
}
//在这里产生了一个新的shim进程,adress地址就是containerd daemon的地址,调用了WithStart func
shimopt = ShimRemote(r.config, r.address, cgroup, exitHandler)
}
// 产生一个shim client
s, err := bundle.NewShimClient(ctx, namespace, shimopt, ropts)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer func() {
if err != nil {
if kerr := s.KillShim(ctx); kerr != nil {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err).Error("failed to kill shim")
}
}
}()
rt := r.config.Runtime
if ropts != nil && ropts.Runtime != "" {
rt = ropts.Runtime
}
//填充 CreateTaskRequest 结构体,发送 GRPC 给 shim 创建,Create 路径为containerd/runtime/v1/shim/service.go
sopts := &shim.CreateTaskRequest{
ID: id,
Bundle: bundle.path,
Runtime: rt,
Stdin: opts.IO.Stdin,
Stdout: opts.IO.Stdout,
Stderr: opts.IO.Stderr,
Terminal: opts.IO.Terminal,
Checkpoint: opts.Checkpoint,
Options: opts.TaskOptions,
}
for _, m := range opts.Rootfs {
sopts.Rootfs = append(sopts.Rootfs, &types.Mount{
Type: m.Type,
Source: m.Source,
Options: m.Options,
})
}
//将创建的请求交给shim处理,我们下边看看shim会再如何处理得到的这个create请求
cr, err := s.Create(ctx, sopts)
if err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.FromGRPC(err)
}
t, err := newTask(id, namespace, int(cr.Pid), s, r.events, r.tasks, bundle)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := r.tasks.Add(ctx, t); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
r.events.Publish(ctx, runtime.TaskCreateEventTopic, &eventstypes.TaskCreate{
ContainerID: sopts.ID,
Bundle: sopts.Bundle,
Rootfs: sopts.Rootfs,
IO: &eventstypes.TaskIO{
Stdin: sopts.Stdin,
Stdout: sopts.Stdout,
Stderr: sopts.Stderr,
Terminal: sopts.Terminal,
},
Checkpoint: sopts.Checkpoint,
Pid: uint32(t.pid),
})
return t, nil
}
func WithStart(binary, address, daemonAddress, cgroup string, debug bool, exitHandler func()) Opt {
return func(ctx context.Context, config shim.Config) (_ shimapi.ShimService, _ io.Closer, err error) {
// 这个address是shim-address,用来containerd和shim进程之间的通信
// filepath.Join(string(filepath.Separator), "containerd-shim", namespace, bundle.id, "shim.sock")
socket, err := newSocket(address)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
defer socket.Close()
f, err := socket.File()
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "failed to get fd for socket %s", address)
}
defer f.Close()
// 执行containerd-shim --namespace default --address /run/containerd/containerd.sock命令
cmd, err := newCommand(binary, daemonAddress, debug, config, f)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
if err := cmd.Start(); err != nil {
return nil, nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "failed to start shim")
}
defer func() {
if err != nil {
cmd.Process.Kill()
}
}()
go func() {
cmd.Wait()
exitHandler()
}()
log.G(ctx).WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"pid": cmd.Process.Pid,
"address": address,
"debug": debug,
}).Infof("shim %s started", binary)
// set shim in cgroup if it is provided
if cgroup != "" {
if err := setCgroup(cgroup, cmd); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
log.G(ctx).WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"pid": cmd.Process.Pid,
"address": address,
}).Infof("shim placed in cgroup %s", cgroup)
}
if err = sys.SetOOMScore(cmd.Process.Pid, sys.OOMScoreMaxKillable); err != nil {
return nil, nil, errors.Wrap(err, "failed to set OOM Score on shim")
}
//通过前边介绍的shim-address产生一个client然后进行通信,使用的也是unix socket通信
c, clo, err := WithConnect(address, func() {})(ctx, config)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, errors.Wrap(err, "failed to connect")
}
return c, clo, nil
}
}
shim处理逻辑
path: containerd/runtime/v1/shim/service.go api list:
type ShimService interface {
State(ctx context.Context, req *StateRequest) (*StateResponse, error)
Create(ctx context.Context, req *CreateTaskRequest) (*CreateTaskResponse, error)
Start(ctx context.Context, req *StartRequest) (*StartResponse, error)
Delete(ctx context.Context, req *google_protobuf1.Empty) (*DeleteResponse, error)
DeleteProcess(ctx context.Context, req *DeleteProcessRequest) (*DeleteResponse, error)
ListPids(ctx context.Context, req *ListPidsRequest) (*ListPidsResponse, error)
Pause(ctx context.Context, req *google_protobuf1.Empty) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
Resume(ctx context.Context, req *google_protobuf1.Empty) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
Checkpoint(ctx context.Context, req *CheckpointTaskRequest) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
Kill(ctx context.Context, req *KillRequest) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
Exec(ctx context.Context, req *ExecProcessRequest) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
ResizePty(ctx context.Context, req *ResizePtyRequest) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
CloseIO(ctx context.Context, req *CloseIORequest) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
ShimInfo(ctx context.Context, req *google_protobuf1.Empty) (*ShimInfoResponse, error)
Update(ctx context.Context, req *UpdateTaskRequest) (*google_protobuf1.Empty, error)
Wait(ctx context.Context, req *WaitRequest) (*WaitResponse, error)
}
// 上文中提到过的CreateRequest通过shim的unix socket交给这个函数来进行处理
// Create a new initial process and container with the underlying OCI runtime
func (s *Service) Create(ctx context.Context, r *shimapi.CreateTaskRequest) (_ *shimapi.CreateTaskResponse, err error) {
s.mu.Lock()
defer s.mu.Unlock()
var mounts []proc.Mount
for _, m := range r.Rootfs {
mounts = append(mounts, proc.Mount{
Type: m.Type,
Source: m.Source,
Target: m.Target,
Options: m.Options,
})
}
config := &proc.CreateConfig{
ID: r.ID,
Bundle: r.Bundle,
Runtime: r.Runtime,
Rootfs: mounts,
Terminal: r.Terminal,
Stdin: r.Stdin,
Stdout: r.Stdout,
Stderr: r.Stderr,
Checkpoint: r.Checkpoint,
ParentCheckpoint: r.ParentCheckpoint,
Options: r.Options,
}
rootfs := filepath.Join(r.Bundle, "rootfs")
defer func() {
if err != nil {
if err2 := mount.UnmountAll(rootfs, 0); err2 != nil {
log.G(ctx).WithError(err2).Warn("Failed to cleanup rootfs mount")
}
}
}()
for _, rm := range mounts {
m := &mount.Mount{
Type: rm.Type,
Source: rm.Source,
Options: rm.Options,
}
if err := m.Mount(rootfs); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Wrapf(err, "failed to mount rootfs component %v", m)
}
}
//下文有介绍
process, err := newInit(
ctx,
s.config.Path,
s.config.WorkDir,
s.config.RuntimeRoot,
s.config.Namespace,
s.config.Criu,
s.config.SystemdCgroup,
s.platform,
config,
)
if err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
//在这里函数里边开始创建物理容器进程
//最终在func (r *Runc) Create(context context.Context, id, bundle string, opts *CreateOpts) 里边通过/run/containerd/runc命令创建符合OCI标准的容器物理进程
if err := process.Create(ctx, config); err != nil {
return nil, errdefs.ToGRPC(err)
}
// save the main task id and bundle to the shim for additional requests
s.id = r.ID
s.bundle = r.Bundle
pid := process.Pid()
s.processes[r.ID] = process
return &shimapi.CreateTaskResponse{
Pid: uint32(pid),
}, nil
}
//在这个func里边返回一个process描述对象供以后使用,这里这里已经是在shim进程里边了。
func newInit(ctx context.Context, path, workDir, runtimeRoot, namespace, criu string, systemdCgroup bool, platform rproc.Platform, r *proc.CreateConfig) (*proc.Init, error) {
var options runctypes.CreateOptions
if r.Options != nil {
v, err := typeurl.UnmarshalAny(r.Options)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
options = *v.(*runctypes.CreateOptions)
}
rootfs := filepath.Join(path, "rootfs")
runtime := proc.NewRunc(runtimeRoot, path, namespace, r.Runtime, criu, systemdCgroup)
//创建进程描述对象,这个时候还没有创建起物理的容器进程
p := proc.New(r.ID, runtime, rproc.Stdio{
Stdin: r.Stdin,
Stdout: r.Stdout,
Stderr: r.Stderr,
Terminal: r.Terminal,
})
p.Bundle = r.Bundle
p.Platform = platform
p.Rootfs = rootfs
p.WorkDir = workDir
p.IoUID = int(options.IoUid)
p.IoGID = int(options.IoGid)
p.NoPivotRoot = options.NoPivotRoot
p.NoNewKeyring = options.NoNewKeyring
return p, nil
}
总结
containerd daemon看起来只是一层比较薄的逻辑。 containerd-shim则相当于是容器物理进程,比如会在容器物理挂掉后接管它,避免它被init进程监管等。 具体的执行还是都交给了底层的runc来完成。
流程图如下所示
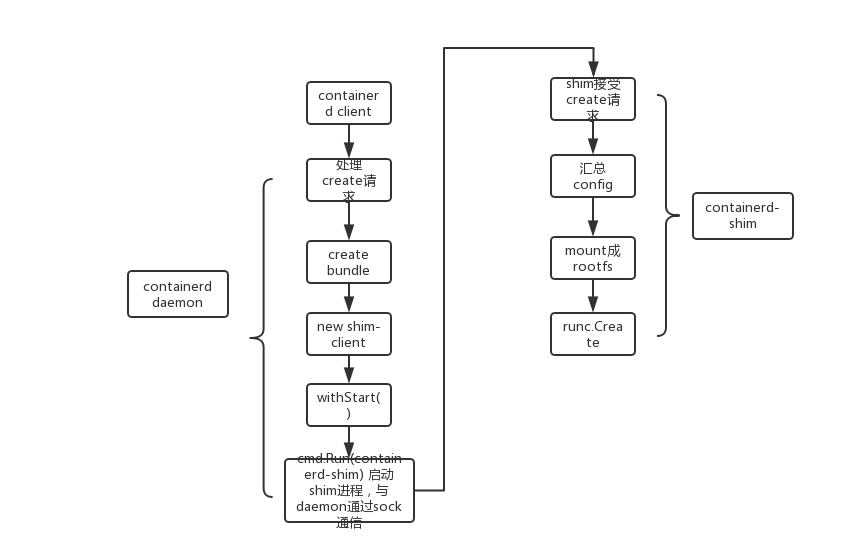
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/zhonglinzhang/article/details/76615127 https://blog.csdn.net/zhonglinzhang/article/category/3271199 https://blog.csdn.net/zhonglinzhang/article/details/76683925