runc
OCI runtime spec
介绍的比较好的文章: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000009583199
https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-spec https://github.com/opencontainers/runtime-tools
runc使用实例
首先通过
$ docker pull busybox $ mkdir -p /tmp/mycontainer/rootfs $ cd /tmp/mycontainer $ docker export $(docker create busybox) | tar -C rootfs -xvf -
产生一个rootfs,当然还可以通过其他的runtime-tools来直接生成
通过runc spec产生一个符合runtime spec的bundle config.json,下边是一个busybox镜像导出的config.json的例子
{
"ociVersion": "1.0.0", //表示进入容器后要执行什么命令,后边还会提到 "process": { "terminal": true, "user": { "uid": 0, "gid": 0 }, "args": [ "sh" ], "env": [ "PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin", "TERM=xterm" ], "cwd": "/", "capabilities": { "bounding": [ "CAP_AUDIT_WRITE", "CAP_KILL", "CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE" ], "effective": [ "CAP_AUDIT_WRITE", "CAP_KILL", "CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE" ], "inheritable": [ "CAP_AUDIT_WRITE", "CAP_KILL", "CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE" ], "permitted": [ "CAP_AUDIT_WRITE", "CAP_KILL", "CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE" ], "ambient": [ "CAP_AUDIT_WRITE", "CAP_KILL", "CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE" ] }, "rlimits": [ { "type": "RLIMIT_NOFILE", "hard": 1024, "soft": 1024 } ], "noNewPrivileges": true }, "root": { "path": "rootfs", "readonly": true }, "hostname": "runc", "mounts": [ { "destination": "/proc", "type": "proc", "source": "proc" }, { "destination": "/dev", "type": "tmpfs", "source": "tmpfs", "options": [ "nosuid", "strictatime", "mode=755", "size=65536k" ] }, { "destination": "/dev/pts", "type": "devpts", "source": "devpts", "options": [ "nosuid", "noexec", "newinstance", "ptmxmode=0666", "mode=0620", "gid=5" ] }, { "destination": "/dev/shm", "type": "tmpfs", "source": "shm", "options": [ "nosuid", "noexec", "nodev", "mode=1777", "size=65536k" ] }, { "destination": "/dev/mqueue", "type": "mqueue", "source": "mqueue", "options": [ "nosuid", "noexec", "nodev" ] }, { "destination": "/sys", "type": "sysfs", "source": "sysfs", "options": [ "nosuid", "noexec", "nodev", "ro" ] }, { "destination": "/sys/fs/cgroup", "type": "cgroup", "source": "cgroup", "options": [ "nosuid", "noexec", "nodev", "relatime", "ro" ] } ], "linux": { "resources": { "devices": [ { "allow": false, "access": "rwm" } ] }, "namespaces": [ { "type": "pid" }, { "type": "network", "path": "/var/run/netns/runc1" }, { "type": "ipc" }, { "type": "uts" }, { "type": "mount" } ], "maskedPaths": [ "/proc/kcore", "/proc/latency_stats", "/proc/timer_list", "/proc/timer_stats", "/proc/sched_debug", "/sys/firmware" ], "readonlyPaths": [ "/proc/asound", "/proc/bus", "/proc/fs", "/proc/irq", "/proc/sys", "/proc/sysrq-trigger" ] }}
runc run启动容器
- runc list查看目前已经有的容器
源码分析
本质上runc是对libContainer的一层封装,将符合OCI的config.json转化为libContainer需要的配置文件,然后通过libContainer将容器启动。
容器创建
path: opencontainers/runc/create.go
Action: func(context *cli.Context) error {
if err := checkArgs(context, 1, exactArgs); err != nil {
return err
}
if err := revisePidFile(context); err != nil {
return err
}
//load config.json到内存来
spec, err := setupSpec(context)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// CT_ACT_CREATE参数,表示首次创建容器
status, err := startContainer(context, spec, CT_ACT_CREATE, nil)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// exit with the container's exit status so any external supervisor is
// notified of the exit with the correct exit status.
os.Exit(status)
return nil
}
func startContainer(context *cli.Context, spec *specs.Spec, action CtAct, criuOpts *libcontainer.CriuOpts) (int, error) {
//获取容器id
id := context.Args().First()
if id == "" {
return -1, errEmptyID
}
notifySocket := newNotifySocket(context, os.Getenv("NOTIFY_SOCKET"), id)
if notifySocket != nil {
//如果systemd支持的话,给容器添加对应的socket通信路径
notifySocket.setupSpec(context, spec)
}
//根据spec中Container相关的内容,调用libcontainer 创建容器对象,且容器的状态设置为Stopped。仅仅只是一个内存中的数据结构,并没有与之对应的进程
container, err := createContainer(context, id, spec)
if err != nil {
return -1, err
}
if notifySocket != nil {
err := notifySocket.setupSocket()
if err != nil {
return -1, err
}
}
// Support on-demand socket activation by passing file descriptors into the container init process.
listenFDs := []*os.File{}
if os.Getenv("LISTEN_FDS") != "" {
listenFDs = activation.Files(false)
}
r := &runner{
enableSubreaper: !context.Bool("no-subreaper"),
shouldDestroy: true,
container: container,
listenFDs: listenFDs,
notifySocket: notifySocket,
consoleSocket: context.String("console-socket"),
detach: context.Bool("detach"),
pidFile: context.String("pid-file"),
preserveFDs: context.Int("preserve-fds"),
action: action,
criuOpts: criuOpts,
init: true,
}
//将spec中的Process转换成libcontainer兼容的模式,并对容器的IO进行配置
return r.run(spec.Process)
}
func (r *runner) run(config *specs.Process) (int, error) {
//检查有关tty的设置,其中的console-socket就是tty mode下需要用的unix-socket
if err := r.checkTerminal(config); err != nil {
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
//将spec的Process转换为libcontainer要求的Process配置格式
process, err := newProcess(*config, r.init)
if err != nil {
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
if len(r.listenFDs) > 0 {
process.Env = append(process.Env, fmt.Sprintf("LISTEN_FDS=%d", len(r.listenFDs)), "LISTEN_PID=1")
process.ExtraFiles = append(process.ExtraFiles, r.listenFDs...)
}
baseFd := 3 + len(process.ExtraFiles)
for i := baseFd; i < baseFd+r.preserveFDs; i++ {
process.ExtraFiles = append(process.ExtraFiles, os.NewFile(uintptr(i), "PreserveFD:"+strconv.Itoa(i)))
}
rootuid, err := r.container.Config().HostRootUID()
if err != nil {
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
rootgid, err := r.container.Config().HostRootGID()
if err != nil {
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
var (
detach = r.detach || (r.action == CT_ACT_CREATE)
)
// Setting up IO is a two stage process. We need to modify process to deal
// with detaching containers, and then we get a tty after the container has
// started.
/
handler := newSignalHandler(r.enableSubreaper, r.notifySocket)
//配置容器I/O,前边有章节专门介绍过
tty, err := setupIO(process, rootuid, rootgid, config.Terminal, detach, r.consoleSocket)
if err != nil {
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
defer tty.Close()
//根据调用方法传入参数的不同,调用不同的执行步骤,在这里就直接start
switch r.action {
case CT_ACT_CREATE:
err = r.container.Start(process)
case CT_ACT_RESTORE:
err = r.container.Restore(process, r.criuOpts)
case CT_ACT_RUN:
err = r.container.Run(process)
default:
panic("Unknown action")
}
if err != nil {
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
//以下都是完成一些start之后的后续工作
if err := tty.waitConsole(); err != nil {
r.terminate(process)
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
if err = tty.ClosePostStart(); err != nil {
r.terminate(process)
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
if r.pidFile != "" {
//为容器创建一个pid-file
if err = createPidFile(r.pidFile, process); err != nil {
r.terminate(process)
r.destroy()
return -1, err
}
}
status, err := handler.forward(process, tty, detach)
if err != nil {
r.terminate(process)
}
if detach {
return 0, nil
}
r.destroy()
return status, err
}
func (c *linuxContainer) Start(process *Process) error {
c.m.Lock()
defer c.m.Unlock()
if process.Init {
// 创建一个路径为/run/runc/$ID/exec.fifo的管道文件
if err := c.createExecFifo(); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// 真正启动容器进程,runc与容器进程之间的通信通过创建的init管道或者环境变量
if err := c.start(process); err != nil {
if process.Init {
//失败了需要删除刚才创建的管道
c.deleteExecFifo()
}
return err
}
return nil
}
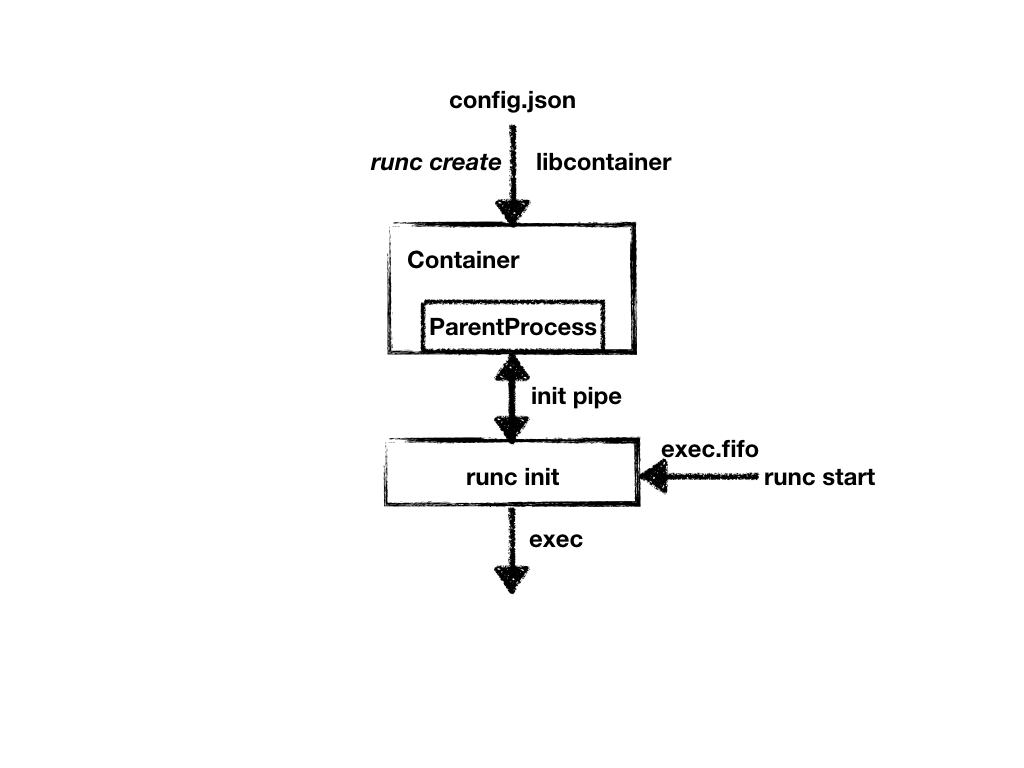
容器进程在产生后必须从runc读取配置才能够继续进行,path: opencontainers/runc/libcontainer/factory_linux.go
func (l *LinuxFactory) StartInitialization() (err error) {
var (
pipefd, fifofd int
consoleSocket *os.File
envInitPipe = os.Getenv("_LIBCONTAINER_INITPIPE")
envFifoFd = os.Getenv("_LIBCONTAINER_FIFOFD")
envConsole = os.Getenv("_LIBCONTAINER_CONSOLE")
)
// Get the INITPIPE.
pipefd, err = strconv.Atoi(envInitPipe)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to convert _LIBCONTAINER_INITPIPE=%s to int: %s", envInitPipe, err)
}
var (
pipe = os.NewFile(uintptr(pipefd), "pipe")
// 判断是`runc create`还是`runc exec`
it = initType(os.Getenv("_LIBCONTAINER_INITTYPE"))
)
defer pipe.Close()
// Only init processes have FIFOFD.
// 只有init进程有FIFOFD
fifofd = -1
if it == initStandard {
if fifofd, err = strconv.Atoi(envFifoFd); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to convert _LIBCONTAINER_FIFOFD=%s to int: %s", envFifoFd, err)
}
}
...
// 会从管道中读取config,然后返回Init的接口对象
i, err := newContainerInit(it, pipe, consoleSocket, fifofd)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// If Init succeeds, syscall.Exec will not return, hence none of the defers will be called.
//下边的代码片段就是展示这个方法
return i.Init()
}
path: opencontainers/runc/libcontainer/standard_init_linux.go
func (l *linuxStandardInit) Init() error {
...
// 配置network, 配置路由等等
...
// 准备rootfs
if err := prepareRootfs(l.pipe, l.config); err != nil {
return err
}
// 配置console, hostname, apparmor, process label, sysctl等等
...
// 告诉父进程我们已经准备好Exec了
if err := syncParentReady(l.pipe); err != nil {
return err
}
// 配置seccomp
...
// 设置正确的capability,用户以及工作目录
if err := finalizeNamespace(l.config); err != nil {
return err
}
...
// 确定用户指定的容器进程在容器文件系统中的路径
name, err := exec.LookPath(l.config.Args[0])
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 关闭init管道,告诉runC进程,我们已经完成了初始化工作
l.pipe.Close()
// 在exec用户进程之前等待exec.fifo管道在另一端被打开
// 我们通过/proc/self/fd/$fd打开它
fd, err := unix.Open(fmt.Sprintf("/proc/self/fd/%d", l.fifoFd), unix.O_WRONLY|unix.O_CLOEXEC, 0)
...
// 向exec.fifo管道写数据,阻塞,直到用户调用`runc start`,读取管道中的数据
if _, err := unix.Write(fd, []byte("0")); err != nil {
return newSystemErrorWithCause(err, "write 0 exec fifo")
}
...
// 调用exec命令,执行用户进程,也就是我们在config文件中看到的process描述的命令
if err := syscall.Exec(name, l.config.Args[0:], os.Environ()); err != nil {
return newSystemErrorWithCause(err, "exec user process")
}
return nil
}
path: opencontainers/runc/libcontainer/rootfs_linux.go
func prepareRootfs(pipe io.ReadWriter, iConfig *initConfig) (err error) {
...
// 配置mounts, dev,将mounts挂载到rootfs等
...
// 通知父进程运行pre-start hooks
if err := syncParentHooks(pipe); err != nil {
return err
}
...
if config.NoPivotRoot {
err = msMoveRoot(config.Rootfs)
} else if config.Namespaces.Contains(configs.NEWNS) {
err = pivotRoot(config.Rootfs)
} else {
//最后还是通过chroot来切换文件系统的视角
err = chroot(config.Rootfs)
}
...
return nil
prepareRootfs先对容器的Mounts和Dev等信息进行配置,之后再调用syncParentHooks,通过init管道向runC进程发送procHooks信号。runC进程接收到procHooks信号之后,执行容器的PreStart Hook回调函数,再通过init管道给容器初始化进程发送信号procResume,通知其继续执行。可见容器的PreStart Hook是在根目录尚未切换之前执行完成的。最终,调用chroot函数,切换根目录。至此,容器的文件系统切换完毕。
在文件系统准备完成之后,Init方法还会对Console, hostname等属性进行配置。当一切就绪之后,调用syncParentReady通过init管道通知runC进程,获取响应之后,关闭init管道,同步结束,准备开始执行用户指定的容器进程。
不过在找到了用户指定的容器程序在容器文件系统的执行路径之后,初始化进程又打开了我们之前多次提到的exec.fifo这个管道,并且往里面写入了一个字节,之后才执行Exec系统调用,切换到用户程序。既然exec.fifo是一个管道,那么我们在这一端写入之后,就必须有消费者在另外一端进行读取,否则写进程就会一直处于阻塞状态。
事实上,此处对exec.fifo管道的写阻塞正是runc create和runc start执行流的分界点。容器的创建工作,在容器初始化进程往exec.fifo管道进行写操作的那一刻,就全部结束了。
容器启动
path: opencontainers/runc/start.go
Action: func(context *cli.Context) error {
if err := checkArgs(context, 1, exactArgs); err != nil {
return err
}
container, err := getContainer(context)
if err != nil {
return err
}
status, err := container.Status()
if err != nil {
return err
}
switch status {
case libcontainer.Created:
// runc start的执行路径到这
return container.Exec()
case libcontainer.Stopped:
return errors.New("cannot start a container that has stopped")
case libcontainer.Running:
return errors.New("cannot start an already running container")
default:
return fmt.Errorf("cannot start a container in the %s state\n", status)
}
}
path: opencontainers/runc/libcontainer/container_linux.go
func (c *linuxContainer) exec() error {
path := filepath.Join(c.root, execFifoFilename)
fifoOpen := make(chan struct{})
select {
case <-awaitProcessExit(c.initProcess.pid(), fifoOpen):
return errors.New("container process is already dead")
//打开fifo,以解开刚才创建容器过程中exec-fifo的写堵塞
case result := <-awaitFifoOpen(path):
close(fifoOpen)
if result.err != nil {
return result.err
}
f := result.file
defer f.Close()
//读取exec-fifo中的内容,也就是刚才写入的那个字节
if err := readFromExecFifo(f); err != nil {
return err
}
return os.Remove(path)
}
}
可是这一路分析下来,似乎并没有对容器的namespace进行配置的操作?事实上,子进程runc init的执行流在进入Go语言的运行时之前,会被包/runc/libcontainer/nsenter劫持,先去执行一段C代码。这段C代码同样会从init管道中读取容器的配置,主要是namespace的路径,clone flag等等,并根据这些配置,调用setns系统调用,将容器进程加入到合适的namespace中。之后再进入Go的运行时,完成上文所述的各种初始化操作。
总结
摘一张来自zju blog的图片